DirectAdmin is a web hosting control panel that allows users to manage their web hosting accounts. Creating an email account in DirectAdmin involves a few simple steps.
- Login to DirectAdmin:
- Open your web browser and go to the DirectAdmin login page provided by your hosting provider.
- Enter your username and password to log in.

- Navigate to Email Accounts:
- Once logged in, look for an option or section related to email accounts. This might be labeled as “Email Accounts,” ” Management,” or something similar.
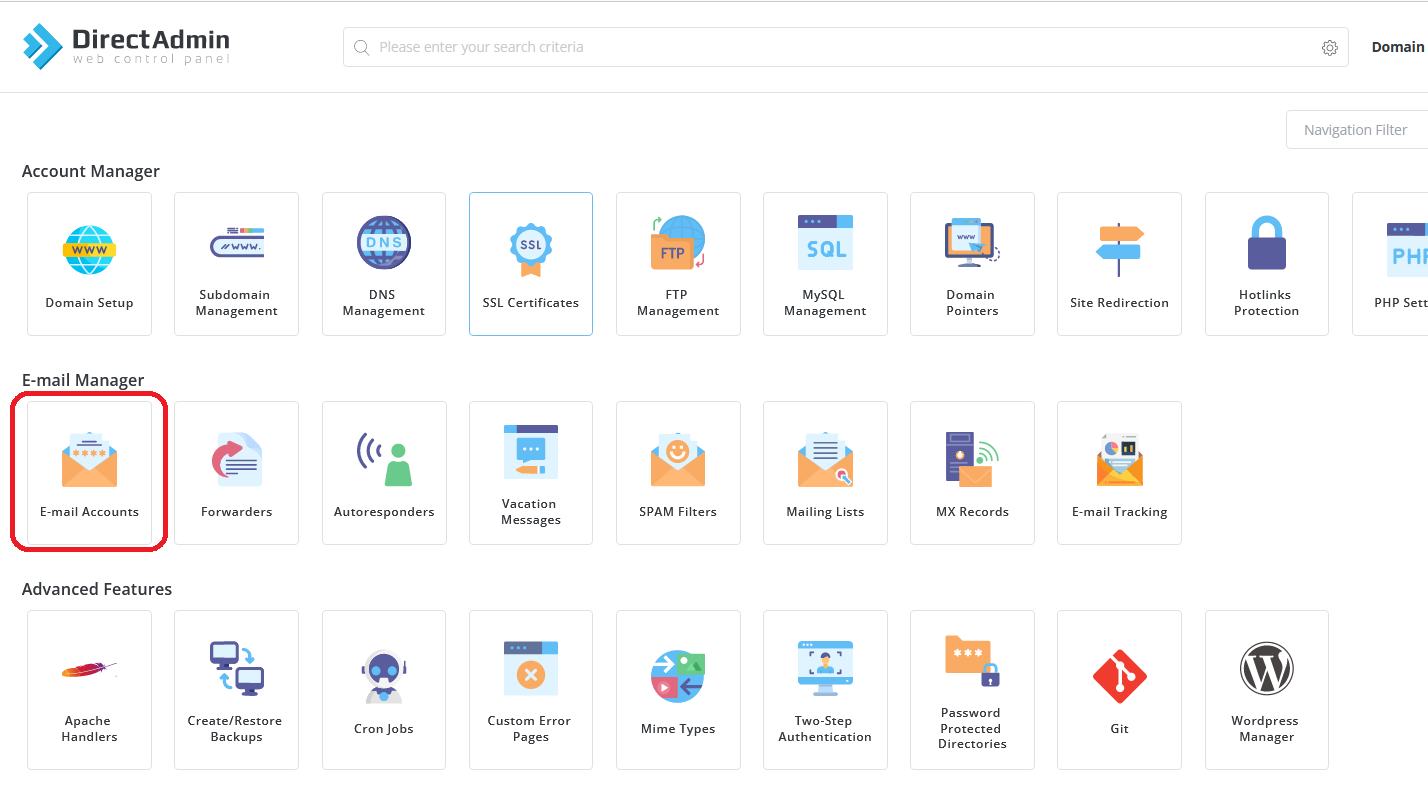
- Once logged in, look for an option or section related to email accounts. This might be labeled as “Email Accounts,” ” Management,” or something similar.
- Create a New Account:
- Find the option to create a new account and click on it.
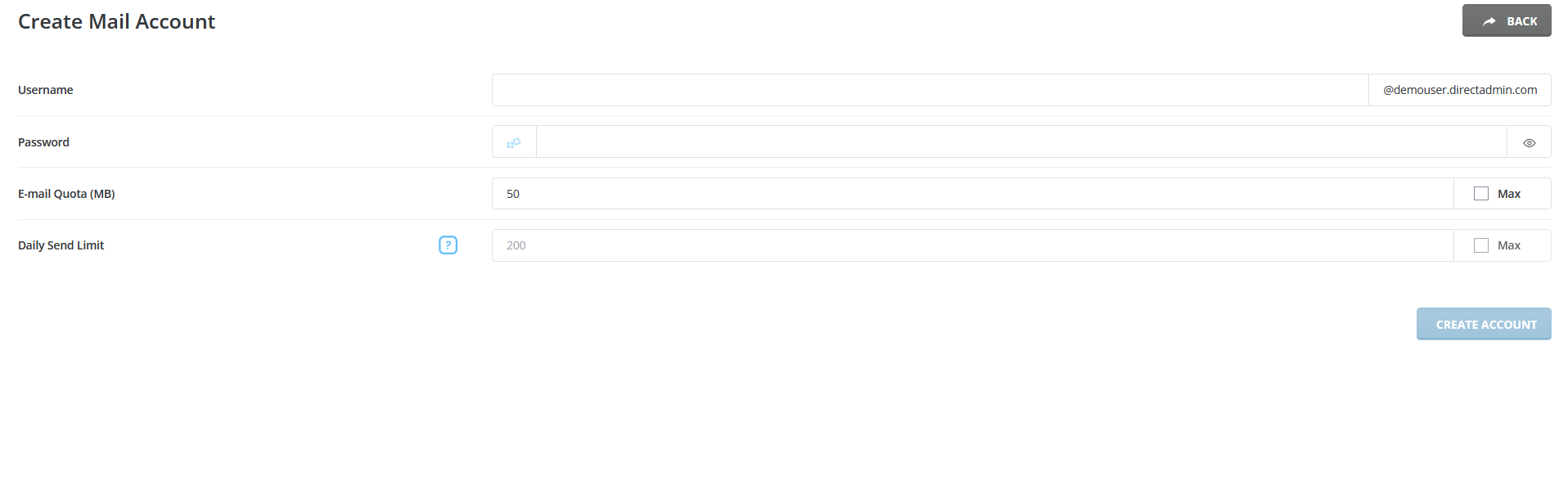
- You will likely be prompted to enter the following information:
- Email Address: The full address you want to create (e.g., yourname@example.com).
- Password: Choose a strong password for the account.
- Quota: Specify the box quota (the amount of disk space allocated to the account).
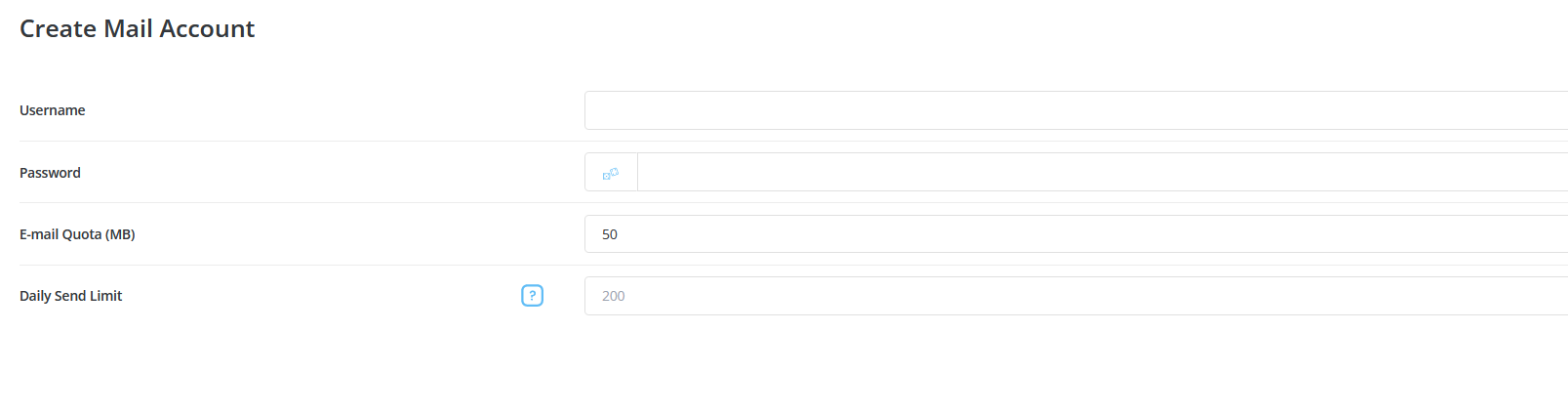
- Configure Additional Settings (Optional):
- Depending on your hosting provider and the specific features offered by DirectAdmin, you may have additional settings to configure, such as forwarding, autoresponders, etc. Follow the on-screen instructions or refer to your hosting provider’s documentation.

- Save or Create the Email Account:
-
- After entering the required information, look for a “Create” or “Save” button. Click on it to create the account
- Access Webmail (Optional):
- Some hosting providers offer a webmail interface that allows you to access your account through a web browser. Check if your provider offers this feature and how to access it.
- Configure Client (Optional):
- If you prefer to use an client (e.g., Outlook, Thunderbird), you’ll need to configure the client with the incoming and outgoing server settings provided by your hosting provider. This information is typically available in the hosting account details or support documentation.
Remember that the exact steps may vary depending on the version and the configuration set by your hosting provider. If you encounter any difficulties or if the interface is different, refer to the documentation provided by your hosting provider or contact their support for assistance.
Certainly! An account is a digital box that allows you to send and receive electronic messages over the internet. It’s a fundamental tool for communication in both personal and professional settings. Here are some key aspects of accounts:
Email Address:
An email address is a unique identifier for an individual’s or organization’s account. It typically consists of a username followed by the “@” symbol and the domain name (e.g., username@example.com).
Inbox:
The inbox is the main folder of your account where incoming messages are stored. When someone sends you an email, it appears in your inbox.
Sent Items:
Sent items are folders where copies of the message you have sent are stored. This helps you keep track of messages you’ve sent.
Drafts:
Drafts are a storage area for message that you have started composing but have not yet sent. You can save drafts and come back to them later.
Spam/Junk Folder:
Most email services have a spam or junk folder that filters out potentially unwanted or unsolicited emails. Messages identified as spam are often automatically moved to this folder.
Trash/Deleted Items:
Deleted items or trash is where deleted are temporarily stored before being permanently removed. Some services allow you to recover deleted items from this folder.
Attachments:
Accounts allow you to send and receive files, documents, or images as attachments to your messages. There is usually a file size limit for attachments.
Contacts:
Services often include a contacts or address book feature where you can store and organize addresses and other contact information.
Settings:
Accounts come with settings that allow you to customize your experience. This includes options for signature, vacation responders, and filtering rules.
Webmail and Clients:
You can access your account through a web browser using web interfaces provided by your service provider. Alternatively, you can configure desktop or mobile clients (e.g., Outlook, Thunderbird) to manage your emails.
Security:
Security is a critical aspect of accounts. Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication if available, and be cautious about phishing attempts to protect your account.


