Let’s Encrypt is a free, automated, and open Certificate Authority (CA) that provides digital certificates for enabling secure (HTTPS) communication on websites. It was launched in 2015 with the goal of making it easier for websites to implement SSL/TLS encryption by providing free and easily obtainable SSL certificates, is the latest certificate authority, which enables you to install a very fundamental and free SSL Certificate recognized by all major browsers like the Akamai, Mozilla, the EFF, CISCO and etc. Besides supporting multiple domains and sub-domains, the initiative provides a secured & automated certificate so that every single website can be guarded with an SSL certificate without having to purchase a new one.

SSL Certificate
Steps to install Let’s Encrypt SSL
Log in to DirectAdmin:
Open your web browser and go to https://yourdomain.com:2222
Log in with your DirectAdmin username and password.

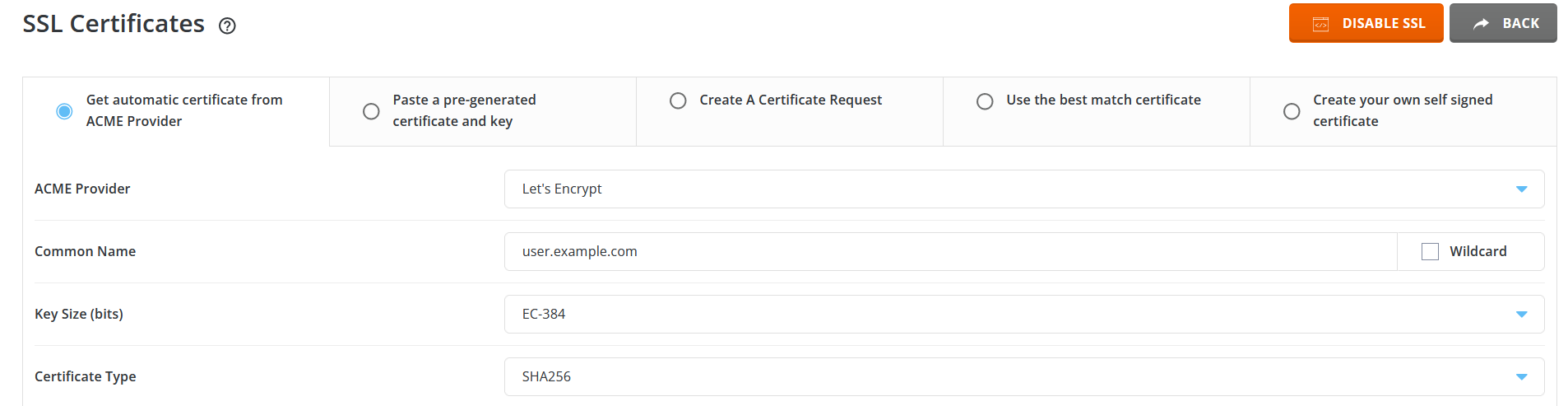
Navigate to SSL Certificates:
Look for an option like “SSL Certificates” or “SSL/TLS Certificates” in the main menu and click on it.

Choose Let’s Encrypt:
Find an option for “Get automatic certificate from ACME Provider” or a similar phrase. Click on it.
Select Domain:
Choose the domain for which you want to generate the SSL certificate. You may also have the option to select subdomains.
Decide whether you want to include ‘www’ in the certificate and whether to secure mail services (POP3, IMAP, SMTP). This depends on your specific requirements.

Submit the Request:
Click on the “Save” or “Request Certificate” button to submit the request to SSL provider.
Verification and Installation:
DirectAdmin will automatically contact SSL provider, validate your domain ownership, generate the SSL certificate, and install it for the selected domain.
Confirm Certificate Installation:
Go back to the SSL Certificates section to verify that the SSL certificate is installed and valid for the chosen domain.
Update Website Configuration:
Ensure that your website’s configuration is updated to use the new SSL certificate. This may involve updating your web server configuration or settings within DirectAdmin.
Force HTTPS (Optional):
If you want to force HTTPS for your website, you can typically do this within your web server or application settings. Some hosting panels, including DirectAdmin, may provide an option for forcing HTTPS.

Verify SSL Installation:
Now you can check the SSL status for your website (https://yourdomainname.com/)
Renewal (Automatic):
Let’s Encrypt certificates have a validity period of 90 days. DirectAdmin usually takes care of the renewal process automatically.
Advantages of Let’s Encrypt:
- Affordability: Let’s Encrypt certificates are free, eliminating financial barriers to implementing HTTPS.
- Security: By providing an easy and automated way to implement SSL/TLS, Let’s Encrypt contributes to a more secure online environment.
- Accessibility: Let’s Encrypt makes encryption accessible to a wide range of websites, promoting the adoption of best security practices.
- Community-driven Development: The open-source nature of Let’s Encrypt encourages collaboration and innovation within the security community.
- Free of Charge: Let’s Encrypt provides SSL/TLS certificates at no cost, making it accessible to website owners of all sizes.
- Automated Certificate Issuance and Renewal: The process of obtaining and renewing certificates is automated, simplifying the traditionally complex task of setting up and maintaining SSL certificates.
- Open Source: The Let’s Encrypt software and protocols are open source, allowing the community to review, contribute, and improve the technology.
- Wildcard Certificates: Let’s Encrypt supports the issuance of wildcard certificates, allowing the secure encryption of a domain and all its subdomains with a single certificate.
- Short Certificate Lifespan: Certificates issued by Let’s Encrypt have a relatively short lifespan of 90 days. This is intentional to encourage frequent updates and renewal, enhancing security.
- ACME Protocol: Let’s Encrypt uses the Automated Certificate Management Environment (ACME) protocol for automating the certificate issuance and renewal processes.
- Community Support: Let’s Encrypt has gained broad community support and is integrated into many web hosting platforms and control panels, making it easier for website owners to enable HTTPS.
How Let’s Encrypt Works:
- Certificate Request: The website owner initiates a certificate request using a client, which generates a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
- Domain Validation: uses automated methods for domain validation, ensuring that the certificate requester has control over the domain for which they are requesting a certificate.
- Certificate Issuance: Once domain ownership is verified, issues the SSL/TLS certificate.
- Installation: The certificate is automatically installed on the web server, and the necessary configurations are updated to enable HTTPS.
- Automatic Renewal: Certificates issued by SSL provider have a short lifespan of 90 days, but the renewal process is typically handled automatically by the client software.
What is an SSL Certificate?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer): SSL is a protocol for establishing secure communication links between a client (like a web browser) and a server. It ensures that the data transmitted between them remains encrypted and secure.
SSL Certificate: An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates the identity of a website and enables a secure connection. It is issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) and contains information about the certificate holder, the public key, the digital signature, and the expiration date.
Components of an SSL Certificate:
Public Key: The public key is embedded in the SSL certificate and is used for encrypting data. It is shared openly and is part of the public-key cryptography system.
Private Key: The private key is known only to the server and is used for decrypting data encrypted with the public key. It must be kept confidential.
Common Name (CN): The Common Name is the domain name for which the certificate is issued (e.g., www.example.com). It helps in identifying the entity the certificate belongs to.
Issuer: The Issuer is the Certificate Authority that issues the SSL certificate. It is a trusted entity that vouches for the authenticity of the certificate.
Validity Period: SSL certificates have a specific validity period during which they are considered valid. Typically, certificates are issued for one to two years.
Digital Signature: The digital signature is a cryptographic hash of the certificate content, signed by the private key of the issuing CA. It ensures the integrity of the certificate.
Types of SSL Certificates:
Domain Validated (DV) Certificates: These certificates verify the ownership of the domain but do not validate the identity of the organization. They are quick to obtain.
Organization Validated (OV) Certificates: OV certificates include validation of the domain ownership and some additional organizational details. They provide a higher level of trust.
Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: EV certificates undergo rigorous validation, including legal and physical checks on the organization. They provide the highest level of assurance, often displayed with a green address bar in browsers.
Wildcard Certificates: Wildcard certificates secure a domain and its subdomains with a single certificate.
Multi-Domain (SAN) Certificates: SAN certificates allow the inclusion of multiple domain names in a single certificate.
Why SSL Certificates are Important:
Data Encryption: SSL ensures that data transmitted between a user’s browser and the server remains confidential and secure.
Trust and Credibility: SSL certificates build trust among users by displaying visual indicators (such as a padlock icon) in the browser address bar.
SEO Benefits: Search engines like Google consider HTTPS as a ranking factor, providing a potential SEO boost to websites with SSL certificates.
Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: SSL prevents attackers from intercepting and tampering with the data during transmission.
Compliance: Many data protection regulations and standards require the use of SSL to protect sensitive information.


